With the advancement of bridge technology, various forms of prestressed concrete beams have been increasingly applied in engineering construction, with T girders being particularly widely used. During construction , it 's common for cracks to form in prestressed concrete T girder, especially after formwork removal and before tensioning the T-girder. This article takes an engineering project as an example to analyze and share preventive and treatment measures for T girder cracks.
The project is located in the southern part of a tropical country. This area has a tropical monsoon climate , similar to summer all year round. The annual average temperature is 28 °C, the average maximum temperature is 31.3 °C, and the average minimum temperature is 23.8 °C. There is no division of four seasons, only the difference between the rainy season and the dry season. The annual rainfall is between 2540 and 5080mm and the climate is humid.
This project spans 30km and the elevated bridge is 10.36km long. The substructure is a 1.8m concrete cast-in-place pile with a single-pile single-column pier structure. The superstructure of the main bridge uses 30m prestressed concrete supported by continuous T-beams. To ensure construction progress, the project has set up multiple precast beam yards near the elevated bridges along the whole line. Most precast beam yards are located in the excavation section. Due to limited land acquisition in some sections, the soft foundation is excavated and replaced after construction of the main line pile foundation, and then the beam yard is constructed.
After removing the first batch of T beams from the formwork in the precast yard, many micro cracks were found on the surface of the T beams.
(1) Classification and treatment methods for cracks. According to the statistical results, most of the crack widths on the site are within 0.2mm and only a few are larger than 0.2mm. At the crack location, the core sampling shows a positive correlation between the crack width and the crack depth. Therefore, cracks are divided into two types based on the standard of 0.2mm: greater than 0.2mm and less than 0.2mm. When the crack width is 0.2mm, the crack depth is about 5mm. The reinforced concrete cover of the T-beam is 40mm thick. Due to the existence of cracks, the effective cover is slightly weakened. Therefore, surface sealing measures have been taken to address these cracks. For cracks with a width greater than 0.2mm, according to the previous analysis, these cracks are not structural cracks but are caused by the plastic deformation of the concrete. When the crack width is between 0.35 - 0.4mm, the crack depth can reach 30 - 35mm, which significantly affects the structure's durability. The treatment of these cracks is the focus of the crack treatment. The common practice for such cracks is grouting treatment.
(2) Requirements and selection of crack repair materials. The requirements for crack repair materials are as follows: ① Good fluidity and low viscosity so as to better penetrate into the cracks; ② High material strength after solidification, at least not lower than the strength of the material to be repaired; ③ Good working performance, able to combine and solidify well with the crack surface in both dry and wet states; ④ High strength and a certain degree of flexibility; ⑤ No shrinkage to avoid separation between the repair material and the material to be repaired. After investigation, epoxy resin materials can meet the above material requirements, so they are selected as the crack surface sealing and grouting materials.
(3) Treatment methods. For cracks less than 0.2mm, use an angle grinder to grind 1mm. If the cracks disappear, no further treatment is necessary. If the cracks still exist after grinding, use epoxy resin slurry to seal them. For cracks with a width greater than 0.2mm, grouting treatment is adopted. The grouting treatment steps are as follows: cleaning the surface cleaning - marking cracks - installing grouting rods , sealing the crack surface - grouting - cleaning the surface sealing material, as shown in Figure 1.
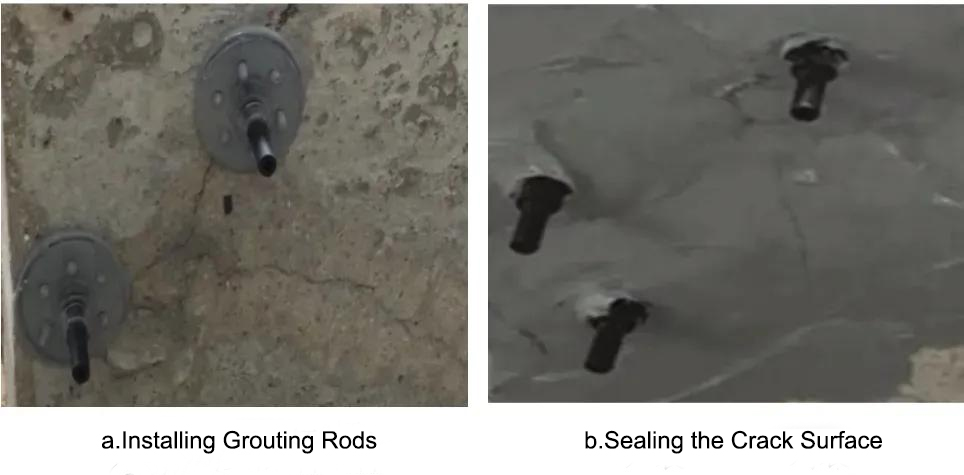

Figure 1
Following the analysis, the following measures are taken to prevent cracks:
(1) Change the concrete pouring time. The concrete pouring time has been changed to the evening when the temperature is lower and the formwork temperature is essentially the same as the concrete temperature.
(2) The sharp corners of the formwork at the joint position between the negative bending moment anchor head and the T-beam top plate, and at the joint position between the diaphragm and the T beam top plate are changed to arcs with a radius of 40mm to reduce stress concentration.
(3) Change the concrete pouring method. Change the method of layered pouring to horizontal layered and oblique segmented pouring to avoid the possibility of construction joints. To avoid stress concentration, change the pouring height as shown in Figure 2.
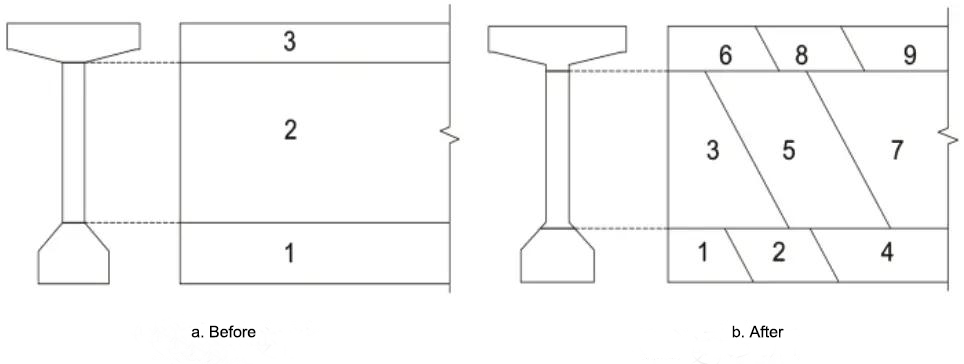
Figure 2 Schematic diagram of the improved concrete pouring sequence for T-beam
(4) Strengthen the maintenance of the T-beams. After applying the maintenance agent on the web and the horse's hoof part, continue to water the top surface of the T beam for more than 7 days to minimize the dry shrinkage of the concrete.
(5) At the diaphragm transition section, change the 200mm reinforcement spacing to 150mm to increase the reinforcement ratio and improve the crack resistance performance of the structure.
Following these measures, cracks on the surface of T-beams are effectively prevented.
There are various causes for the occurrence of T girder cracks. The potential causes of cracks should be listed one by one based on the specific project situation and analyzed one by one to arrive at a reliable conclusion.
To sum up, based on the analysis and treatment of T-beam cracks in this project, the following suggestions are put forward:
(1) In areas with small annual temperature changes, the self - shrinkage stress of concrete is the main cause of T - beam cracks.
(2) Pay attention to the handling of construction details during construction to prevent stress concentration.
(3) Adopt reasonable construction techniques during construction, enhance concrete maintenance, and reduce concrete shrinkage.
(4) T-beams must be treated to ensure the safety and durability of the structure.

International Department: Room 2211-2212, Tower C of Wanda Plaza, Tongzhou District, Beijing 101118, China.
+86-13021287080
info@boyoun.cn